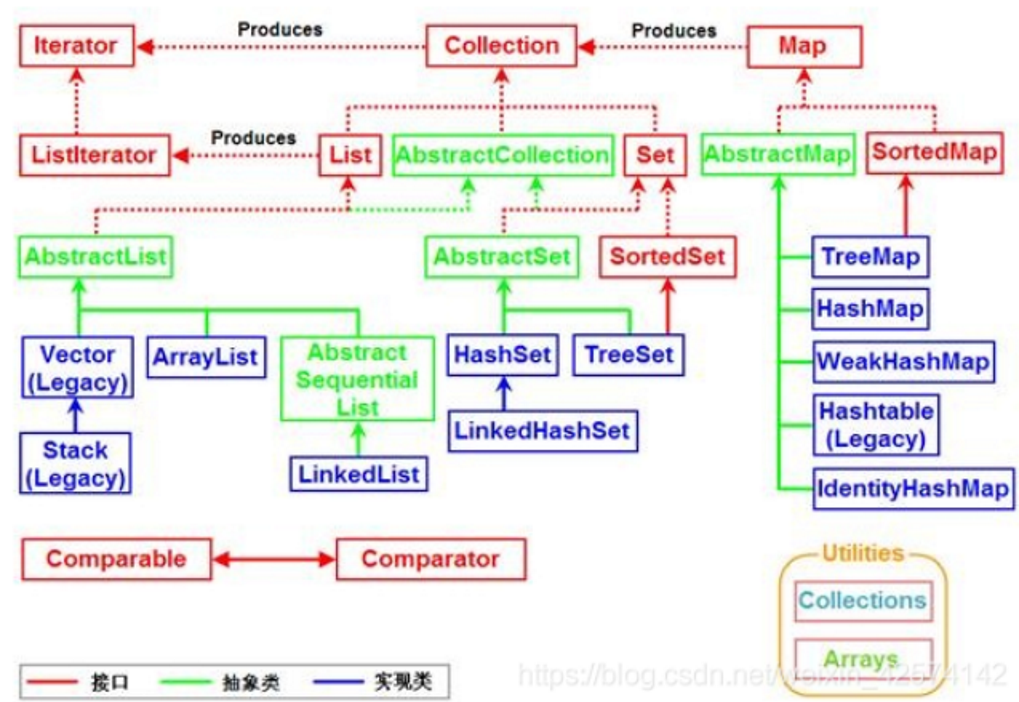
STL库继承图
ArrayList和LinkedList
Arraylist
关于Arraylist的源码分析(动态变化数组)
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10;
默认空间为10;
数据存放处
transient Object[] elementData;
ensureCapacity方法
int minExpand = (elementData != DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA)
// any size if not default element table
? 0
// larger than default for default empty table. It's already
// supposed to be at default size.
: DEFAULT_CAPACITY;
当elementData不是默认容量 minExpand = 0:否则 =默认容量
get方法(检查给定索引是否在范围内。如果不是,则引发适当的运行时异常。此方法 * 不 * 检查索引是否为负: 它总是在数组访问之前立即使用,如果索引为负,则抛出 ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException。)
public E get(int index) {
rangeCheck(index);
return elementData(index);
}
可动态变化原因ensureCapacityInternal:(将指定的元素追加到此列表的末尾)
public boolean add(E e) {
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
elementData[size++] = e;
return true;
}
当加入超过
private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) {
ensureExplicitCapacity(calculateCapacity(elementData, minCapacity));
}
private static int calculateCapacity(Object[] elementData, int minCapacity) {
if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) {
return Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity);
}
return minCapacity;
}
private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) {
modCount++;
// overflow-conscious code
if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)
grow(minCapacity);
}
grow 重新构建copy到newCapacity大小重新赋值elementData
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
// minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win:
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
minCapacity 扩展到原有大小*2-1
MAX_ARRAY_SIZE:Integer.MAX_ALUE -8
将现在大小+现在大小/2的数作为基础 minCapacity
minCapacity>MAX_ARRAY_SIZE 到达上限,取int型上限
private static int hugeCapacity(int minCapacity) {
if (minCapacity < 0) // overflow
throw new OutOfMemoryError();
return (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) ?
Integer.MAX_VALUE :
MAX_ARRAY_SIZE;
}
Arrays.copyof()
public static <T,U> T[] copyOf(U[] original, int newLength, Class<? extends T[]> newType) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
T[] copy = ((Object)newType == (Object)Object[].class)
? (T[]) new Object[newLength]
: (T[]) Array.newInstance(newType.getComponentType(), newLength);
System.arraycopy(original, 0, copy, 0,
Math.min(original.length, newLength));
return copy;
}
按传递来数据的类型创建长度为newLength的对象数组,通过arraycopy复制数据
public static native void arraycopy(Object src, int srcPos,Object dest, int destPos,int length);
将会调用c语言完成高效的数组复制
从头构造方法看
构造一个初始容量大小为 initialCapacity 的 ArrayList
public ArrayList(Collection<? extends E> c) {
Object[] a = c.toArray();
if ((size = a.length) != 0) {
if (c.getClass() == ArrayList.class) {
elementData = a;
} else {
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(a, size, Object[].class);
}
} else {
// replace with empty array.
elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
}
}
使用指定Collection 来构造 ArrayList 的构造函数
public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) {
if (initialCapacity > 0) {
this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];
} else if (initialCapacity == 0) {
this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+
initialCapacity);
}
}
LinkedList:数组
linkedlist是由链表组成的Node类组成的
private static class Node<E> {
E item;
Node<E> next;
Node<E> prev;
Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) {
this.item = element;
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;
}
}
主要元素是
transient序列化
transient int size = 0;
transient Node<E> first;
transient Node<E> last;
size 链表长度,first链表头,last链表尾
get方法
public E getFirst() {
final Node<E> f = first;
if (f == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return f.item;
}
public E getLast() {
final Node<E> l = last;
if (l == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return l.item;
}
remove删除方法
public E removeFirst() {
final Node<E> f = first;
if (f == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return unlinkFirst(f);
}
public E removeLast() {
final Node<E> l = last;
if (l == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return unlinkLast(l);
}
add添加
public void addFirst(E e) {
linkFirst(e);
}
public void addLast(E e) {
linkLast(e);
}
public boolean add(E e) {
linkLast(e);
return true;
}
Vector和Stack
vector
同arraylist可变数组增长原理一样
主要元素
//元素
protected Object[] elementData;
//大小
protected int elementCount;
/**向量的容量在其大小超过其容量时自动增加的数量。如果容量增量小于或等于零,则向量的容量在每次需要增长时都会增加一倍。*/
protected int capacityIncrement;
变化方法
private void ensureCapacityHelper(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)
grow(minCapacity);
}
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + ((capacityIncrement > 0) ?
capacityIncrement : oldCapacity);
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
构造函数
public Vector(int initialCapacity, int capacityIncrement) {
super();
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+
initialCapacity);
this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];
this.capacityIncrement = capacityIncrement;
}
initialCapacity:表示初始大小
capacityIncrement:表示增长步长,默认值0
capacity:不为0则为原本数的2倍
同步锁 新增
public synchronized void addElement(E obj) {
modCount++;
ensureCapacityHelper(elementCount + 1);
elementData[elementCount++] = obj;
}
同步锁 删除
public synchronized void removeElementAt(int index) {
modCount++;
if (index >= elementCount) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index + " >= " +
elementCount);
}
else if (index < 0) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);
}
int j = elementCount - index - 1;
if (j > 0) {
System.arraycopy(elementData, index + 1, elementData, index, j);
}
elementCount--;
elementData[elementCount] = null; /* to let gc do its work */
}
stack
继承Vector的更改
入栈
public E push(E item) {
addElement(item);
return item;
}
出栈
public synchronized E pop() {
E obj;
int len = size();
obj = peek();
removeElementAt(len - 1);
return obj;
}
hash
见链接文档